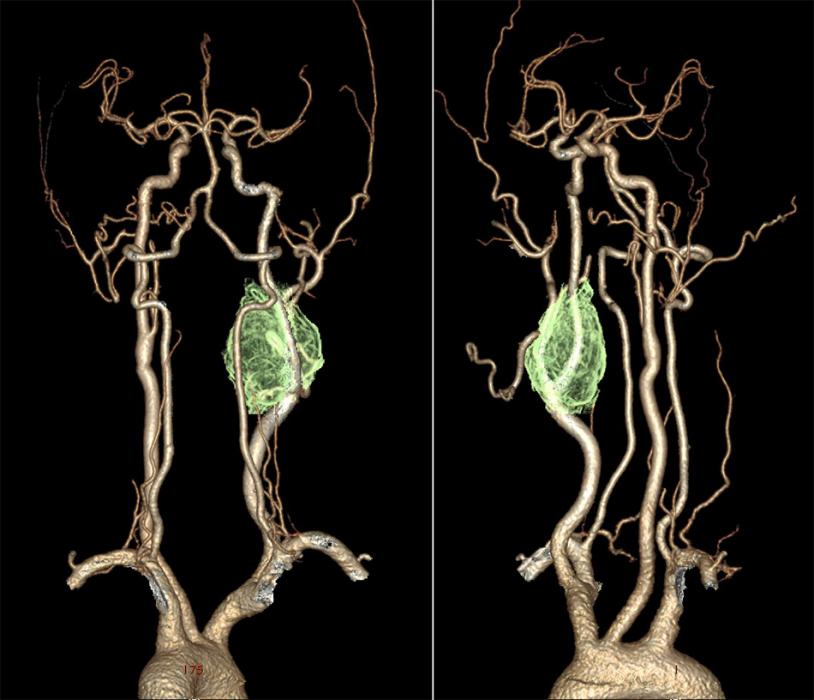
41-year-old male patient from Darjeeling, presented with complaints of painless, non-progressive swelling over the right side of the neck for the past 8 years with paroxysmal paresthesia over the right ear for the past 8 months.
He had a history of similar swelling on the left side for which he was evaluated and underwent surgical excision a few years before. His younger brother aged 32 also have a similar swelling, which was detected recently and for which evaluation is pending.
He is an occasional consumer of alcohol. No comorbidities.
General examination
- Pulse rate 80/minute. All peripheral pulses present.
- Blood pressure 132/80 mmHg
Local examination
- Single, smooth pulsatile mass of 3×3 cm present in the right carotid triangle. The skin over the swelling appears stretched. No color changes, discharging sinuses or dilated veins.
- On palpation, the mass is firm, non-tender with transverse mobility and restricted vertical mobility.
- The swelling became less prominent on contracting deep cervical fascia and sternocleidomastoid.
- No other neck swellings palpable.
- Healed scar present on right side of the neck.
- Gag reflex present.
- Rest of the systemic examination was unremarkable.
Questions
- What is your provisional diagnosis?